How to Tell if a Diamond Is Real: 12 At-Home and Professional Tests
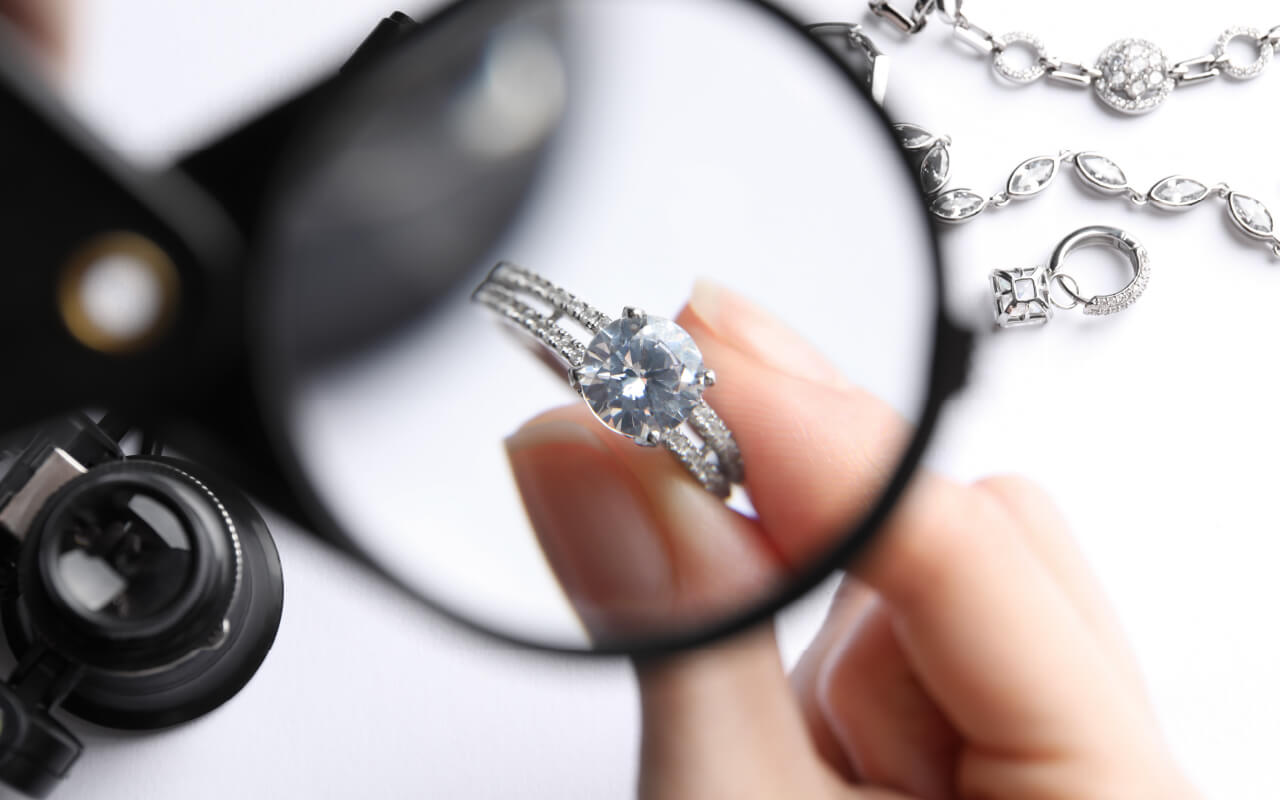

Learn easy ways to verify a diamond’s authenticity at home or with a professional so you can buy and wear your jewelry with confidence.
Diamonds are prized for their brilliance, durability and symbolism, but with so many convincing imitators, it’s natural to wonder if yours is real. From cubic zirconia to moissanite, simulants can mimic a diamond’s sparkle but never its unmatched light performance or lasting value.
Even when buying or inheriting pieces from other sources, knowing how to verify authenticity can give you extra confidence in your jewelry. In this guide, we’ll show you how to tell if a diamond is real through 12 reliable tests, including easy at-home checks and professional evaluations performed by jewelers.
At Blue Nile, every natural and lab-grown diamond we sell is real, responsibly sourced and independently graded by leading labs such as GIA and IGI. To see how real diamonds catch and reflect light, explore a few of our most-loved pieces below.
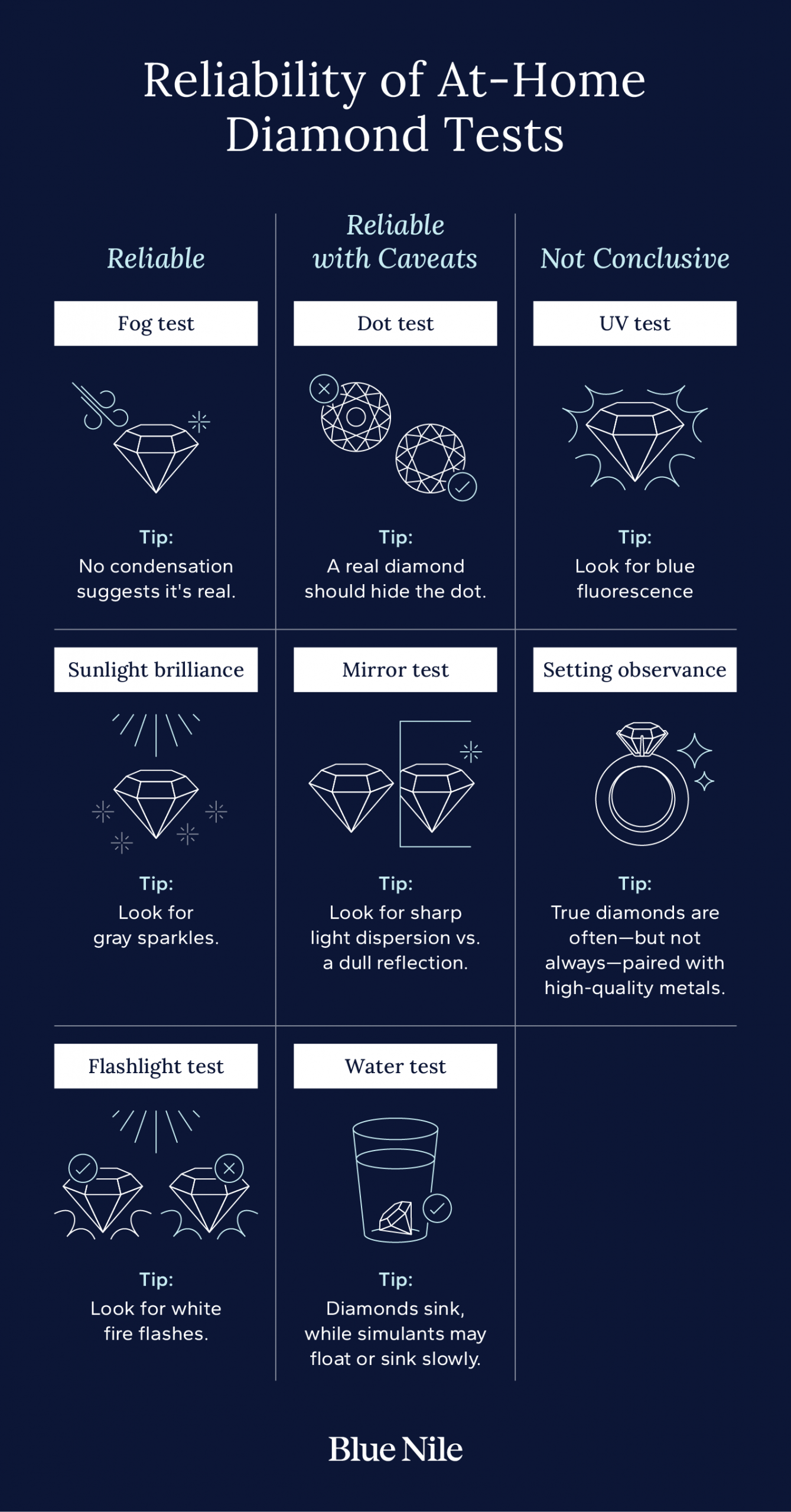
1. Fog Test
Diamond test type: Home test
The fog test is one of the most popular techniques for telling if a diamond is real at home. Simply hold the jewelry to your mouth and exhale on the stone like you‘re trying to fog a mirror. A real diamond will quickly dissipate any condensation from your breath, while simulants will often stay fogged for a few seconds.
2. Sunlight Brilliance Test
Diamond test type: Home test
The unique brilliance of diamonds is part of what has made these gems so popular for centuries. A real diamond in sunlight usually sparkles in shades of gray with intense light.
Other gems like moissanite will show mostly rainbow sparkle, creating an easy comparison of real diamond sparkle vs. fake. A highly polished jewelry-quality gemstone that has a dull sparkle is likely not a diamond.
3. Flashlight Test
Diamond test type: Home test
To learn how to tell if a diamond is real with a flashlight, shine the light through the stone or onto its surface. A genuine diamond bends and scatters light in many directions, producing sharp white reflections and colorful flashes known as fire.
Simulants like glass or cubic zirconia usually let light pass straight through or appear hazy and uniform under direct light. While this isn’t a definitive test, it can provide a quick visual cue about your diamond’s authenticity.
4. Dot Test
Diamond test type: Home test
This test for telling if a diamond is real measures the refractivity of your gemstone and is best done with an unmounted diamond. A real diamond is exceptionally refractive.
For this test, draw a small dot on a piece of paper and place your diamond over the dot you’ve drawn. A real diamond will typically have high refraction, which makes it difficult to see the dot through the stone. It’s important to note that diamond cut plays a role in this test, as some diamonds with less-ideal cuts may be less refractive.
5. Mirror Test
Diamond test type: Home test
For this test, place the stone flat side down on a mirror and notice how it interacts with the reflected light. A real diamond’s facets will scatter light sharply, showing bright flashes rather than a single focused reflection.
Simulants such as glass or cubic zirconia often allow light to pass cleanly through, producing a dull or uniform reflection. While the mirror test alone can’t confirm authenticity, it’s another quick way to compare how a genuine diamond handles light versus imitation stones.
6. Water Test
Diamond test type: Home test
The water test is another technique for testing if an unmounted diamond is real. Both lab–grown and natural diamonds are heavier than diamond fakes such as glass and quartz. This means that in general, a diamond will sink when dropped into a small glass of water. Glass and quartz, on the other hand, may sink slowly or even float.
This isn’t a foolproof technique for how to tell if a diamond is real, though, as some simulants like cubic zirconia may sink quickly as well.
7. UV Test
Diamond test type: Home test
Under ultraviolet (UV) light, many—but not all—natural diamonds emit a soft blue glow called fluorescence. Lab-grown diamonds may display weaker or no fluorescence, and some natural diamonds don’t fluoresce at all.
Simulants typically appear yellowish or remain unchanged under UV light. This test can offer an additional clue, but because fluorescence varies, it shouldn’t be used as the only indicator of whether a diamond is real.
8. Setting Observance Test
Diamond test type: Home test
Your jewelry setting can tell you a lot about the quality of any gems in the piece. Typically, real diamonds will be set in metals like gold or platinum. If the jewelry is silver or gold plated, it may feature a diamond simulant instead.
The technique for determining diamond authenticity based on the type of jewelry metal may not apply to custom pieces or vintage jewelry, so it’s important to check your gemstones with additional methods.

9. Loupe Test
Diamond test type: Professional jeweler test
A jeweler’s loupe magnifies the fine details that reveal how to tell a real diamond by eye. Under 10x magnification, a genuine diamond often shows natural inclusions or subtle internal features, while simulants appear flawless or have rounded facet edges.
Professionals also use a loupe to study the diamond’s facet symmetry and polish, details that can help distinguish a real stone from a convincing imitation.
10. Weight Test
Diamond test type: Professional jeweler test
Because diamonds are denser than most imitation stones, jewelers can weigh and compare them to known standards. Two gems of the same size may differ noticeably in carat weight, with a real diamond typically weighing less than lookalikes like cubic zirconia. This density difference is subtle, so the test requires a precision scale and an expert familiar with standard carat-to-size ratios.
11. Diamond Tester Tool
Diamond test type: Professional jeweler test
A diamond tester measures how a stone conducts heat or electricity, two physical properties that help identify a real diamond. When the probe touches the surface, a genuine diamond quickly disperses heat and registers as authentic.
Jewelers rely on specialized testers to measure how a stone conducts heat or electricity. These professional instruments offer precise results and can distinguish natural and lab-grown diamonds from common simulants.
12. Diamond Certificate
Diamond test type: Professional jeweler test
The most reliable way to confirm a diamond’s authenticity is through an independent grading report from a trusted gemological laboratory.
Certificates from organizations such as the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) or the International Gemological Institute (IGI) verify that a diamond’s 4Cs—cut, color, clarity and carat weight—have been professionally assessed. These documents provide the clearest proof when comparing a real vs. fake diamond, ensuring confidence in your purchase and its long-term value.
How to Spot Diamond Lookalikes
Some imitation gemstones share a diamond’s sparkle, but their features reveal key differences. Paying attention to how each stone reflects light and varies in density can help you spot substitutes before buying or repairing jewelry. If you collect antique or heirloom pieces like vintage rings, check to make sure the diamonds weren’t swapped out over the years.
Common characteristics of popular diamond alternatives include:
- Cubic zirconia: Softer, heavier and shows rainbow flashes rather than bright white sparkle
- Moissanite: Extremely brilliant, but its rainbow fire appears exaggerated and colorful
- White sapphire: Less refractive and tends to look hazy or glassy in bright light
- Glass or crystal: Easily scratched and lacks the crisp facet edges of a real diamond
- Spinel or topaz: Naturally occurring gems that can mimic colorless diamonds but lack hardness and scintillation
Buy Real Diamonds through Blue Nile
Knowing how to tell if a diamond is real helps you shop with confidence, whether you’re evaluating a new purchase or verifying a cherished heirloom.
At Blue Nile, we offer only authentic, responsibly sourced diamonds that are expertly graded and certified for quality. Explore our extensive collection of real diamonds to learn about different cuts, compare natural and lab-grown options and see how grading reports confirm authenticity.
When you’re ready to make your selection, our diamond experts can help you choose the perfect piece. Browse our engagement rings, diamond earrings, necklaces and bracelets to find jewelry you’ll treasure for a lifetime.
FAQ about How to Tell if a Diamond Is Real
Can you test a diamond with your phone?
You can use your phone’s flashlight, or any bright light, as a quick way to observe how a diamond interacts with light. A real diamond typically reflects sharp white flashes and subtle hints of color, but simulants can appear hazy or overly rainbow-like. Because this method isn’t conclusive, it’s best used as a casual observation rather than a definitive test of authenticity.
How do you tell if a ring is real or fake?
There are several ways to check whether a diamond ring is authentic, from assessing the materials used to examining the craftsmanship and sparkle. Consider these key indicators of a genuine diamond ring:
- Metal quality stamps: Genuine pieces are often marked “PT,” “PLT,” “18k” or “14k.”
- Stone behavior: A real diamond refracts light sharply, showing bright white and subtle rainbow flashes rather than a hazy glow.
- Craftsmanship: Prongs and settings should feel sturdy and precise, not thin or uneven.
- Certification: Authentic diamond rings come with a grading report from a trusted lab such as GIA or IGI.
Because visual cues alone can be misleading, the most reliable way to confirm authenticity is to have the ring evaluated by a professional jeweler.
How to tell if a mounted diamond is real?
Some tests, like the dot test and water test, are best done with unmounted diamonds. But you can still inspect your mounted stone to tell if it’s real with other tests. Try the fog or flashlight test to learn more about your stone. Jewelers can test mounted stones using diamond testers.
The setting of your jewelry can also offer some clues to whether you have a real or fake diamond. Real diamonds are often set in precious metals like gold rings, while fake diamonds are often found in more inexpensive settings.
Why should I know if a diamond is real or not?
Understanding whether a diamond is real helps protect both its sentimental and financial value. Authentic stones retain their brilliance and durability over time, while imitations can lose clarity or scratch easily.
Confirming authenticity also ensures that your jewelry can be properly valued and insured—for example, through comprehensive engagement ring insurance.
What should I look for when buying a real diamond?
A genuine diamond’s quality is defined by the 4Cs—cut, color, clarity and carat—along with grading from a trusted gemological lab. Prioritize an ideal cut for maximum brilliance and review diamond certification reports to confirm authenticity.
Shoppers can also explore detailed guides on areas of interest, such as buying diamond studs and engagement ring diamond types, to learn more about shapes, settings and overall craftsmanship.





![GIA 1.00 Carat Cushion Modified Diamond]](https://bluenile-blog.r2net.com/wp-content/uploads/download-300x238.png)


